Proteins are biomacromolecules, consisting of 20 different amino acids, the basic building blocks of living organisms, linked into chains by peptide bonds. Proteins carry out a wide range of functions, based on the order and numbers of amino acids (sequences) that determine their characteristics. In order for proteins to function correctly, the information on sequences of amino acids coded in genes must be translated into polypeptides (long peptide chains) in a “translation device” called the ribosome. The chain is subsequently folded into a specific 3-D structure, allowing the protein to carry out its proper function.
![]()
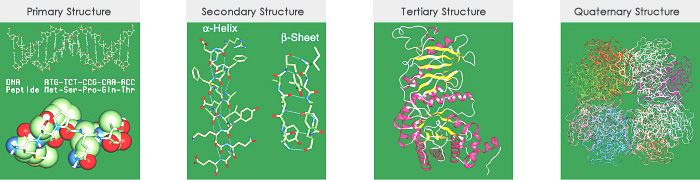
The structure of a protein can be described using four hierarchical structures: amino acid sequences determined by the genetic code (primary structure), characteristic structures such as ƒ¿-helices and ƒÀ-sheets formed by polypeptides or chains of amino acids (secondary structure), and the 3-D structure of the protein, which includes the alignment of the secondary structures (ƒ¿-helices and ƒÀ-sheets) formed by one polypeptide chain comprising a protein (tertiary structure). For some proteins, the interaction of two or more polypeptide chains can be described as a higher level of structure (quaternary structure).